U.S. Coast Guard Response to Chinese Research Vessel in U.S. Arctic Waters
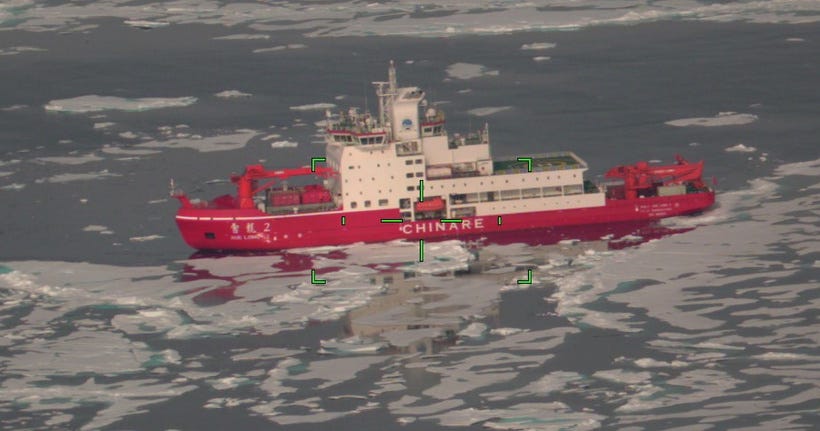
China operates three icebreakers, including Xue Long, Xue Long 2, and Zhong Shan Da Xue Ji Di, supporting dual civil-military research in the Arctic.
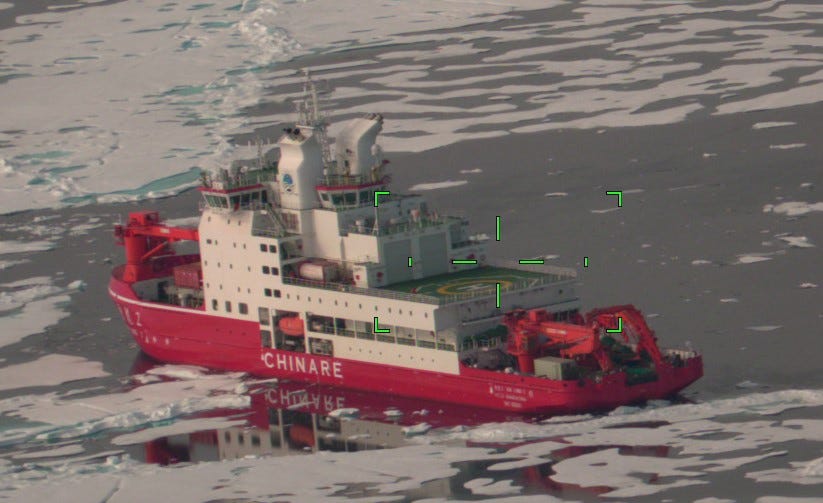
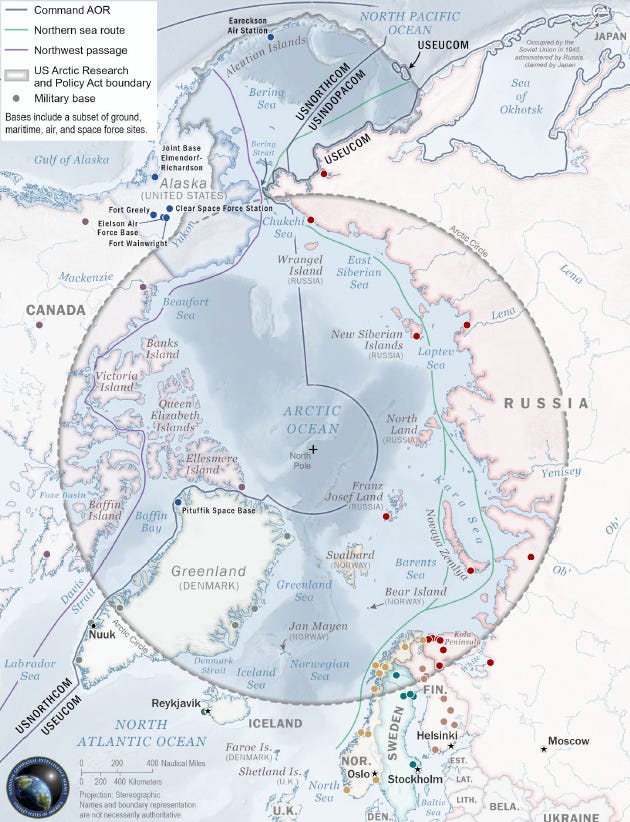
ARCTIC — On Friday, the U.S. Coast Guard detected and responded to the China-flagged research ship Xue Long 2 operating on the U.S. Extended Continental Shelf approximately 290 nautical miles north of Utqiagvik, Alaska.
A Coast Guard C-130J Hercules aircraft from Air Station Kodiak conducted the response, locating the vessel 130 nautical miles inside the ECS boundary.
The Xue Long 2 is an icebreaker operated by the Polar Research Institute of China. This activity occurred under Operation Frontier Sentinel, which aims to maintain presence in response to foreign vessel operations in or near Alaskan waters.
The incident aligns with established protocols for monitoring foreign activities in U.S. waters. The U.S. asserts exclusive rights over its ECS for resource management, consistent with international frameworks.
What Is The U.S. Extended Continental Shelf?
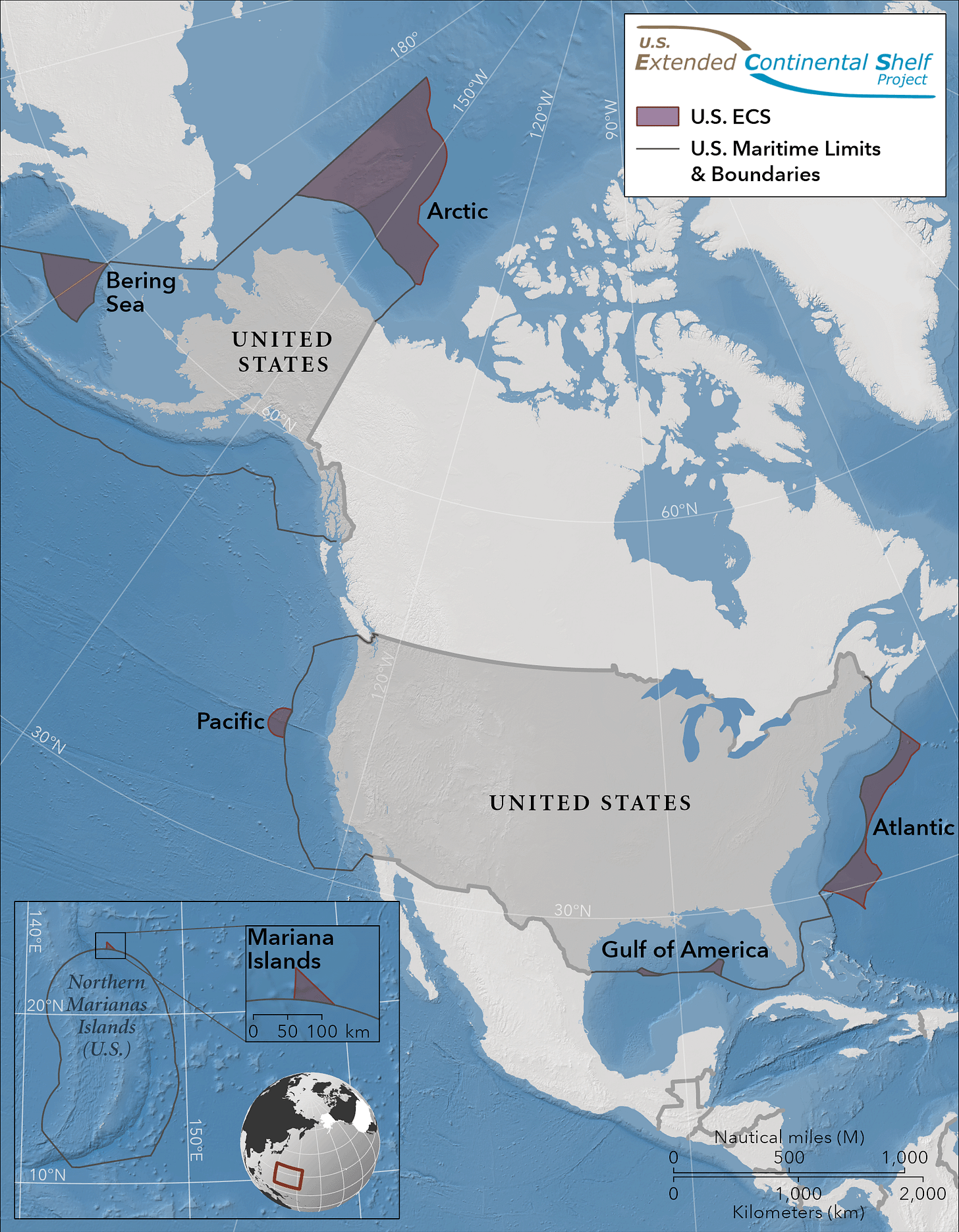
According to the U.S. Department of State, “the United States has ECS in seven offshore areas (Figure 1): the Arctic, Atlantic (east coast), Bering Sea, Pacific (west coast), Mariana Islands, and two areas in the Gulf of America.”
“The U.S. ECS area is approximately one million square kilometers – an area about twice the size of California. The United States may also have ECS in other areas, and the U.S. ECS Project continues to analyze available data and undertake analysis in a range of areas.”
The attached Executive Summary provides information on the outer limits of the U.S. continental shelf in areas beyond 200 nautical miles from the territorial sea baselines (referred to as the “extended continental shelf”).
The United States has delineated these outer limits in accordance with the relevant provisions of the 1982 United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea (Convention) and the Scientific and Technical Guidelines of the Commission on the Limits of the Continental Shelf.
The U.S. continental shelf, including the extended continental shelf (ECS), is considered U.S. territory under international law, though with some limitations. The coastal state exercises sovereign rights over its continental shelf for resource exploration and exploitation.
The U.S. has delineated the outer limits of its continental shelf, including the ECS, and claims sovereign rights over resources in this area.